Water is undeniably the lifeblood of agriculture. Proper and efficient water management is absolutely critical for achieving optimal crop growth and development, ensuring the effective uptake of essential nutrients from the soil, and ultimately maximizing overall crop yields. In contrast, inefficient irrigation practices can lead to significant water wastage, degradation of valuable soil resources through erosion and salinization, and a substantial reduction in agricultural productivity. Implementing sustainable and effective water management practices tailored to specific farm conditions and crop requirements is essential.
“Water is the driving force of all nature.” – Leonardo da Vinci
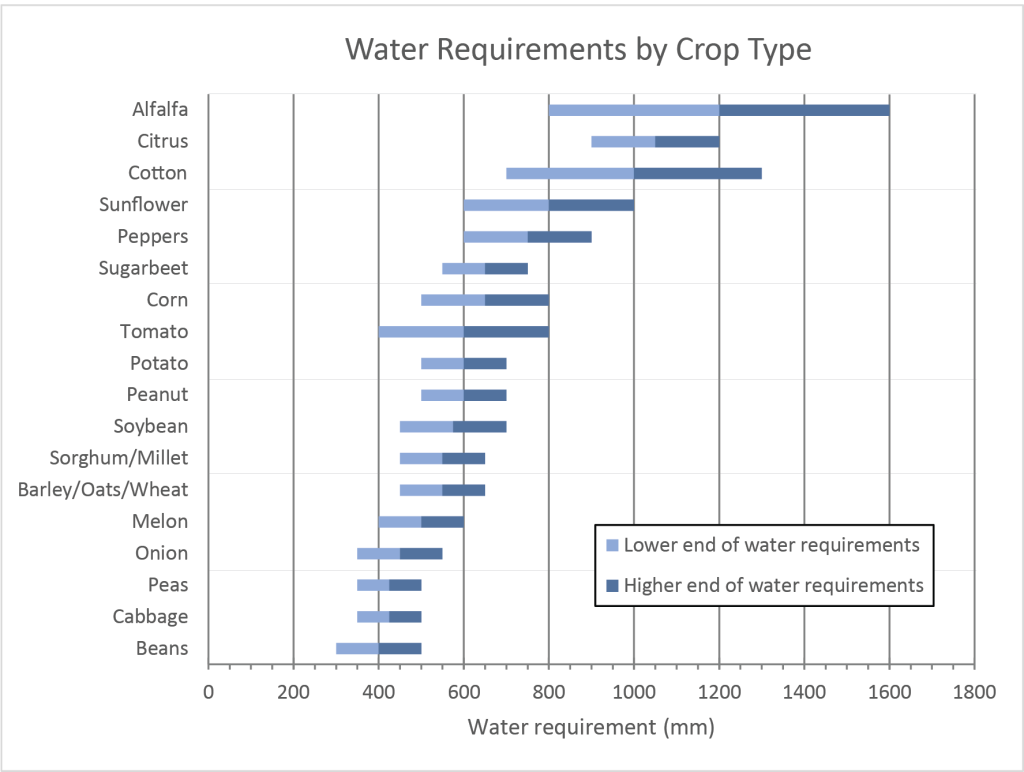
1. Understanding Crop Water Requirements: Matching Supply to Demand
Different types of crops have varying water needs depending on their specific growth stage (from seedling to maturity), the prevailing climatic conditions (temperature, humidity, rainfall patterns), and the characteristics of the soil in which they are grown (water-holding capacity). Farmers should strive to understand the unique water requirements of their specific crops at each stage of development. This detailed understanding forms the basis for developing optimized irrigation schedules that ensure plants receive the right amount of water at the right time, maximizing growth and minimizing water stress.
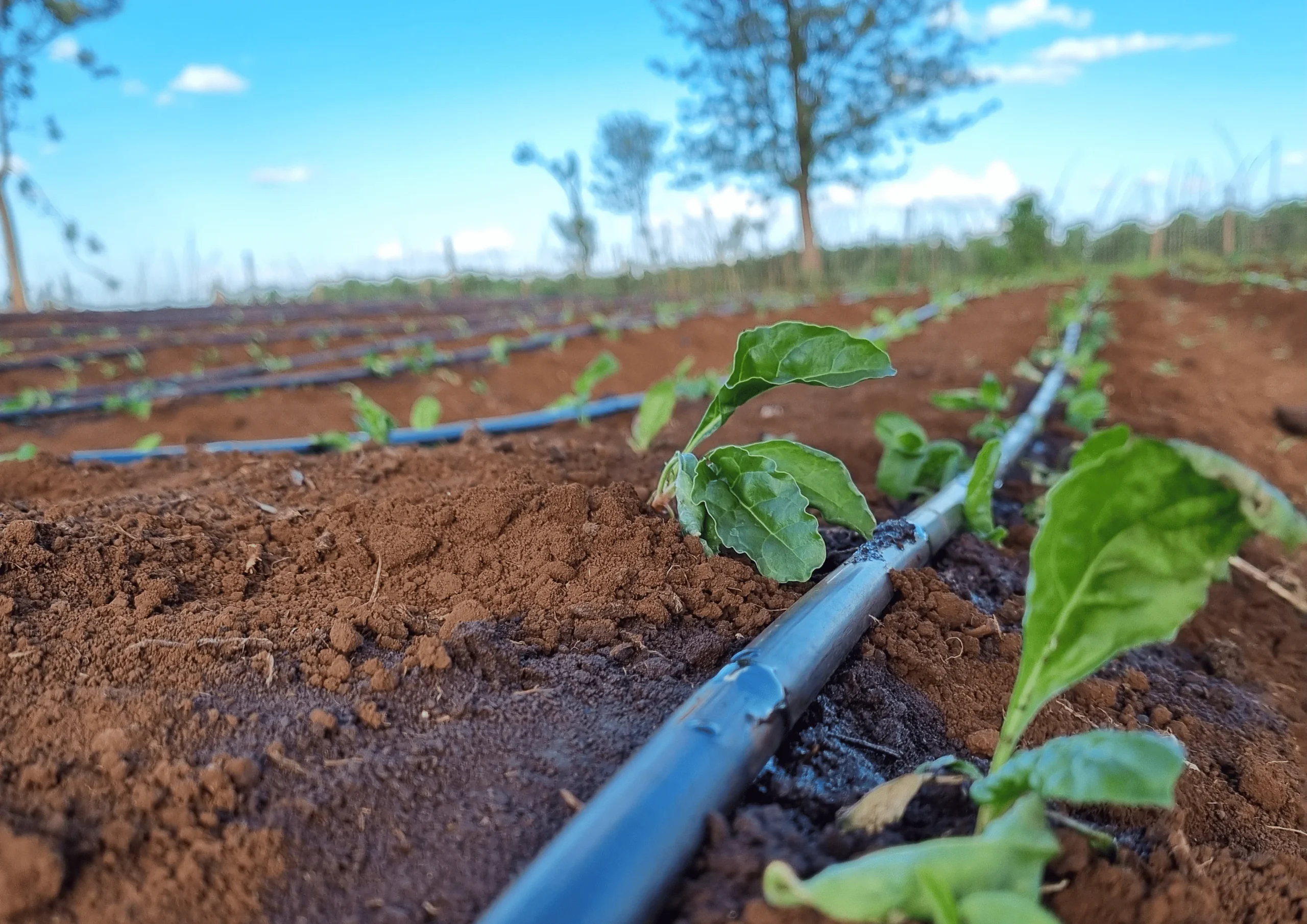
2. Efficient Irrigation Systems: Making Every Precious Drop Count
Traditional flood irrigation methods, while sometimes simple to implement, can often be highly inefficient, leading to significant losses of precious water through surface evaporation, excessive runoff, and deep percolation below the root zone. Modern and efficient irrigation systems, such as drip irrigation (which delivers water slowly and directly to the plant roots through a network of tubes and emitters) and micro-sprinklers (which apply water in a localized spray pattern), offer significantly higher water use efficiency. These systems minimize water loss and ensure that the applied water is effectively utilized by the plants, leading to substantial water savings and improved crop performance.
3. Water Conservation Techniques: Beyond Efficient Application
In addition to adopting efficient irrigation systems, a range of other valuable techniques can be implemented to further enhance water conservation in agricultural practices. These include the application of mulches (organic or synthetic materials spread on the soil surface) to reduce evaporation from the soil, the implementation of rainwater harvesting systems to capture and utilize rainfall, and the improvement of the soil’s natural water-holding capacity through the incorporation of organic matter, which acts like a sponge.

4. Monitoring Soil Moisture: Irrigating Based on Actual Need
Relying solely on fixed irrigation schedules, without considering the actual moisture content of the soil, can often lead to either over-watering (which can waterlog roots and leach nutrients) or under-watering (which can stress plants and reduce yields). Implementing effective soil moisture monitoring techniques, using either sophisticated soil moisture sensors or simple manual methods (such as the “feel” method), allows farmers to gain a real-time understanding of the water availability in the root zone. This enables them to irrigate only when it’s truly needed and to apply the precise amount of water required, optimizing water use efficiency and promoting healthy plant growth.
5. Addressing Waterlogging and Drainage Issues: Preventing Root Suffocation
While water scarcity is a critical concern in many agricultural regions, excessive water in the soil can also be highly detrimental to crop growth. Poor soil drainage can lead to waterlogging, a condition where the soil becomes saturated with water, displacing oxygen from the soil pores. This lack of oxygen suffocates plant roots, hindering their ability to absorb essential nutrients and ultimately leading to stunted growth and even plant death. Implementing appropriate drainage solutions, such as installing drainage tiles or creating surface drainage channels, is crucial to prevent waterlogging and ensure healthy root development.
Effective water management is a cornerstone of productive and sustainable agriculture, contributing to resource conservation and optimal crop yields.






